Stats 140SL Final Project: Forecasting NBA player salaries from their performance in the previous year
Lecture 1 Team 2
Christine Marie Castle, Alan Ha, Hortencia Mendoza, Julian van Riet, Chenzhijian Yan, Caleb Yuan
Poster
Introduction
The National Basketball Association (NBA) is a professional basketball league in the United States and Canada. However, is it really possible to predict NBA players’ salaries based on their performances?
After each season, NBA team rosters undergo many changes due to free agency and trade deals. Distinguished players often have a higher value and achieve this status through their in-game performances.
In order to gain more insight on the relationship between NBA players’ performances and their salaries and investigate how a player’s performance one year affects their salary in the next year, we have chosen each NBA player’s stats associated with their performances in the 2018-2019 season from RealGM and each NBA player’s salary in the 2019-2020 season from ESPN.
In this study, we analyze the data of NBA players’ performances to predict their salaries in the next year. By building a statistical model, we explore the insights of how large an impact each element of NBA players’ performances has on their next year salaries. Furthermore, with the data of each NBA player’s salary from ESPN, we are able to examine how closely NBA players’ performances are related to their salaries.
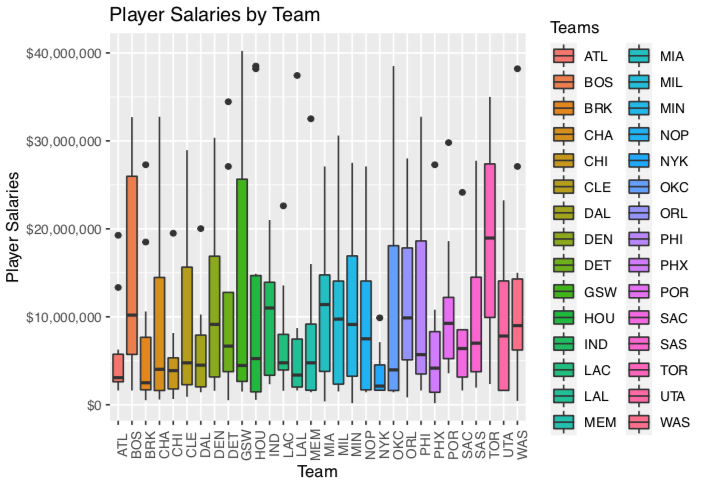
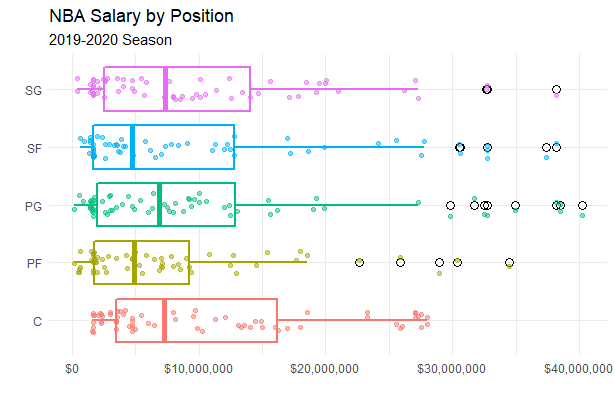
Hypothesis
Our null hypothesis is that we will not be able to predict NBA players’ salaries based on the stats of their previous seasons, since there are many underlying factors involved besides performance.
Methods
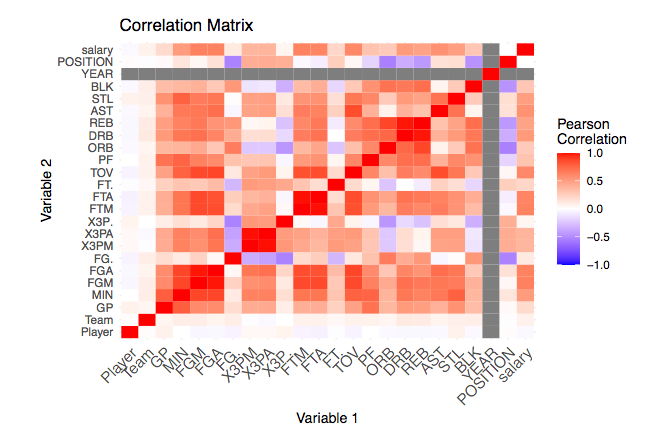
We removed linear combinations and correlated variables from our data set to reduce multicollinearity. Then we performed best subset selection with Mallows’ Cp and Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) to find the most significant features. We randomly selected 70\% of the players to train a multiple linear regression model using 10 predictors:
Salary ~ Team + Position + GP + FGA + 3PM + FTM + TOV + DRB + AST + BLK
We found that games played, free throws made, and assists were the most significant predictors.

Results and Conclusions
Our model achieved an R-squared of 67.29\% and an adjusted R-squared of 59.96\%. Using our model, we made predictions on the remaining 30\% of athletes. The result was an RMSE of $7.7 million.
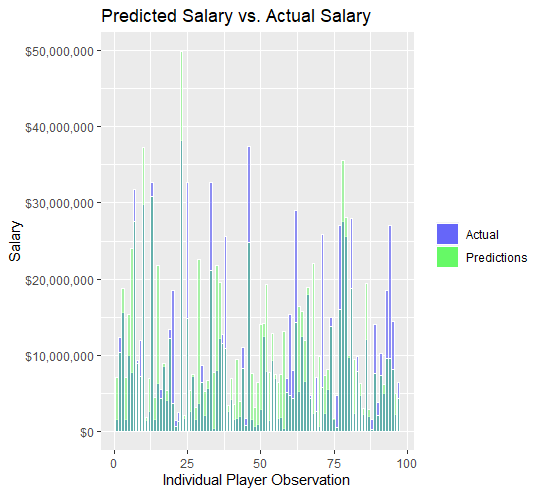

Limitations and Next Steps
Although we obtained a decent R-squared, limitations in our model include missing some players’ salary data as well as not taking into consideration the variation in each teams’ budget. Some teams may have more budget to work with and can therefore pay their players’ more, meanwhile other teams can not.
Our model assumes that a players’ salary contract is determined only by their performance in their previous season. However, this is not always the case as they could be two years into their contract and their salary was determined by their performance years ago.
References
- RealGM 2018-2019 NBA Player Stats https://basketball.realgm.com/nba/stats/2019/Totals/Qualified/points/All/desc/1/Regular_Season
- ESPN 2019-2020 NBA Player Salaries http://www.espn.com/nba/salaries/_/year/2020/seasontype/4